CARG Health Devices: Simulation and Modeling of Physiological Devices and Systems
The CARG team works on creating simulations and models for health-related devices and systems. Our goal is to make biomedical devices work better and more efficiently using advanced computational methods.
Motivation
CARG is motivated by the need to make health monitoring devices more accurate and reliable. By developing models and simulations, we aim to understand and improve how these devices interact with the human body.
Current Research
Here are some of their recent projects:
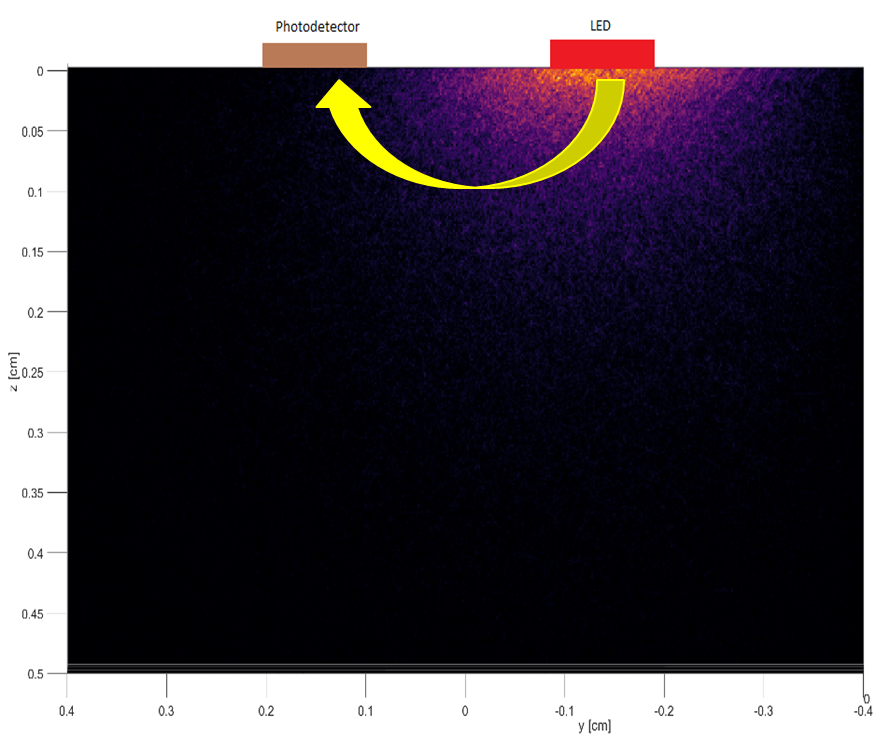
- Model based device design: We’re using simulations to improve the design and performance of devices that monitor cardiovascular and respiratory systems. For example, we explored how skin tone and other factors impact the accuracy of pulse oximeters.
- CPAP and Heart Function: They studied how CPAP (a common therapy for sleep apnea) affects the heart. Interestingly, while CPAP can reduce cardiac output mechanically, it also increases it by reducing afterload.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, CARG wants to:
- Personalize Health Monitoring: We’re working on models that adapt to individual differences, making devices more accurate for everyone, regardless of their unique physiology.
- Use AI in Modeling: By integrating artificial intelligence, they hope to better predict how devices will perform and how they’ll affect patients.
- Build Real-Time Feedback Systems: They aim to create devices that can give immediate feedback to patients and healthcare providers, making healthcare decisions faster and better.
Motivation
Research Papers
- Yoshida, M, Dajani, HR, Ando, S, Shimizu, S, Bolic, M, Groza, V. Analysis of the effect of CPAP on hemodynamics using clinical data and a theoretical model: CPAP therapy decreases cardiac output mechanically but increases it via afterload. Sleep Medicine, 2024.
- - Description: Analysis of the effect of CPAP on hemodynamics using clinical data and a theoretical model: CPAP therapy decreases cardiac output mechanically but increases it via afterload published in Sleep Medicine.
Read More- Bolic, M. Simulating the Effects of Melanin and Air Gap Depth on the Accuracy of Reflectance Pulse Oximeters. In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2023) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 64-71 ISBN: 978-989-758-631-6; ISSN: 2184-4305.
- - Description: Evaluates the effects of skin color on the accuracy of oxygen saturation estimates.
Read More- Bolic, M. Pervasive Cardiovascular and Respiratory Monitoring Devices: Model-Based Design, 2023.
- - Description: The book about modeling and simulation of biomedical devices.
Read More- Olhosseiny, H. H., Mirzaloo, M., Bolic, M., Dajani, H. R., Groza, V., Yoshida, M.. Identifying High Risk of Atherosclerosis Using Deep Learning and Ensemble Learning. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), 2021.
- - Description: The paper presents a classification of patients based on physiological signals.
Read MoreResearchers
External Collaborators
Alumni